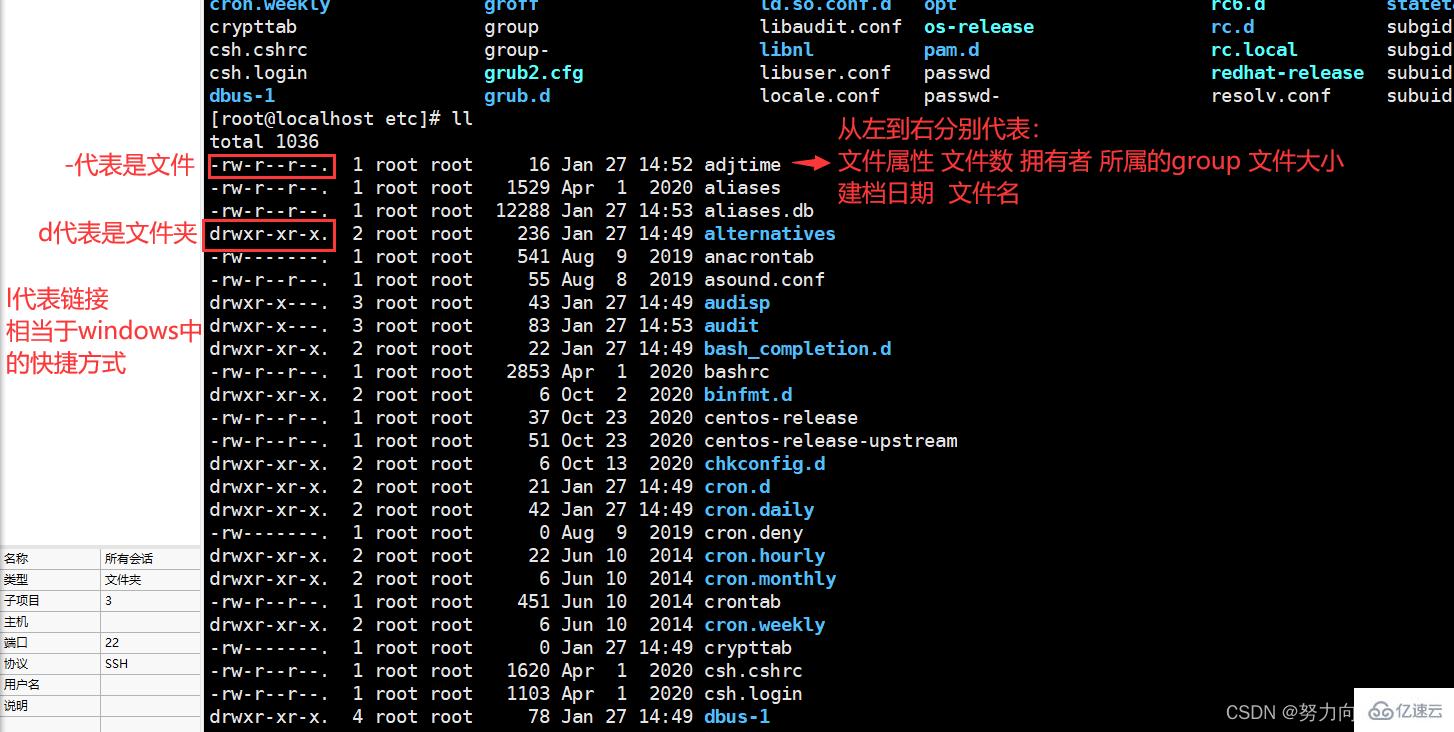
linux如何进入文件目录
- Linux
- 2025-08-08
- 22
cd 命令。
Linux操作系统中,进入文件目录是一项基本而重要的操作,以下是几种常用的方法来进入或导航到特定的文件目录:
使用cd命令
cd是“change directory”的缩写,用于改变当前工作目录。
-
进入特定目录:
cd /path/to/directory
要进入
/home/user/Documents目录,可以输入:cd /home/user/Documents
-
进入上一级目录:
cd ..
-
进入当前用户的主目录:
cd ~
-
进入当前目录的子目录:
如果已经在/home/user目录下,并且想进入Documents子目录,可以直接输入:cd Documents
使用绝对路径和相对路径
- 绝对路径:从根目录开始的完整路径。
/home/user/Documents。 - 相对路径:相对于当前目录的路径,如果当前在
/home/user目录下,那么Documents就是一个相对路径。
使用pushd和popd命令
这两个命令可以保存和恢复目录栈,方便在多个目录之间快速切换。
-
保存当前目录并进入新目录:
pushd /path/to/new/directory
-
返回到之前保存的目录:
popd
使用ls命令查看目录内容
在进入目录之前,通常需要知道该目录是否存在以及其中包含哪些文件和子目录。ls命令用于列出目录内容。
-
列出当前目录的内容:
ls
-
列出指定目录的内容:
ls /path/to/directory
使用pwd命令查看当前目录
pwd是“print working directory”的缩写,用于显示当前所在的工作目录。
pwd
使用mkdir命令创建新目录
如果目标目录不存在,可以使用mkdir命令创建它。
mkdir /path/to/new/directory
使用rmdir命令删除空目录
如果不再需要某个空目录,可以使用rmdir命令删除它。
rmdir /path/to/empty/directory
使用cp、mv和rm命令管理文件和目录
-
复制文件或目录:
cp source_file destination_file cp -r source_directory destination_directory
-
移动或重命名文件或目录:
mv source_file destination_file mv source_directory destination_directory
-
删除文件或目录:
rm file_name rm -r directory_name
使用find命令查找文件或目录
如果不确定文件或目录的具体位置,可以使用find命令进行搜索。
find /search/path -name "filename"
使用locate命令快速查找文件或目录
locate命令利用系统的索引数据库快速查找文件或目录,但需要定期更新数据库。
locate filename
使用ln命令创建链接
链接分为硬链接和软链接(符号链接),它们都可以指向文件或目录。
-
创建硬链接:
ln source_file hard_link_name
-
创建软链接:
ln -s source_file symbolic_link_name
使用chmod和chown命令更改权限和所有权
-
更改文件或目录的权限:
chmod permissions file_name
给所有用户读写权限:
chmod a+rw file_name
-
更改文件或目录的所有权:
chown user:group file_name
使用du和df命令查看磁盘使用情况
-
查看文件或目录的磁盘使用情况:
du -sh /path/to/directory
-
查看文件系统的磁盘空间使用情况:
df -h
使用tar和gzip等命令打包和解包文件
-
打包目录为tar文件:
tar -cvf archive.tar /path/to/directory
-
解包tar文件:
tar -xvf archive.tar
-
压缩并打包目录为tar.gz文件:
tar -czvf archive.tar.gz /path/to/directory
-
解压缩并解包tar.gz文件:
tar -xzvf archive.tar.gz
使用scp和rsync命令远程传输文件和目录
-
使用scp传输文件或目录:
scp source_file user@remote_host:/path/to/destination
-
使用rsync同步文件或目录:
rsync -avz source_directory user@remote_host:/path/to/destination
使用mount和umount命令挂载和卸载文件系统
-
挂载设备或镜像到目录:
mount /dev/device /path/to/mountpoint
-
卸载已挂载的文件系统:
umount /path/to/mountpoint
使用df和free命令查看系统资源使用情况
-
查看磁盘空间使用情况:
df -h
-
查看内存使用情况:
free -h
使用top和htop命令监控系统进程和资源使用情况
-
使用top命令:
top
-
使用htop命令(需要先安装):
htop
使用ps和kill命令管理进程
-
查看当前运行的进程:
ps aux
-
终止特定进程:
kill process_id
使用history命令查看命令历史记录
history
使用alias和unalias命令管理别名
-
创建别名:
alias alias_name='command'
-
删除别名:
unalias alias_name
使用echo和cat命令查看和创建文件内容
-
显示文本到终端:
echo "Hello, World!"
-
查看文件内容:
cat file_name
-
创建或追加文本到文件:
echo "text" > file_name # 覆盖文件内容 echo "text" >> file_name # 追加到文件末尾