上一篇
Java操作txt文件方法?
- 后端开发
- 2025-06-08
- 2482
在Java中读取txt文件,常用
BufferedReader或
Files类实现,通过
FileReader创建文件流,结合
BufferedReader逐行读取;或直接用
Files.readAllLines()一次性加载所有行,注意处理
IOException和关闭资源(try-with-resources自动管理)。
在Java中打开并读取.txt文件是常见的I/O操作,以下是详细方法及最佳实践,涵盖多种场景:
核心方法及代码示例
使用 BufferedReader + FileReader(经典逐行读)
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.FileReader;
import java.io.IOException;
public class ReadTxtFile {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String filePath = "example.txt";
try (BufferedReader reader = new BufferedReader(new FileReader(filePath))) {
String line;
while ((line = reader.readLine()) != null) {
System.out.println(line); // 处理每行内容
}
} catch (IOException e) { // 捕获文件不存在或读取错误
System.err.println("读取文件失败: " + e.getMessage());
}
}
}
优势:
- 高效缓冲机制,适合大文件
readLine()自动处理换行符
使用 Files 类(Java 7+ 推荐)
import java.nio.file.Files;
import java.nio.file.Paths;
import java.util.List;
import java.io.IOException;
public class ReadTxtFile {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String filePath = "example.txt";
try {
// 一次性读取所有行(小文件适用)
List<String> lines = Files.readAllLines(Paths.get(filePath));
for (String line : lines) {
System.out.println(line);
}
// 或逐行流式处理(大文件优化)
Files.lines(Paths.get(filePath)).forEach(System.out::println);
} catch (IOException e) {
System.err.println("错误: " + e.getMessage());
}
}
}
优势:
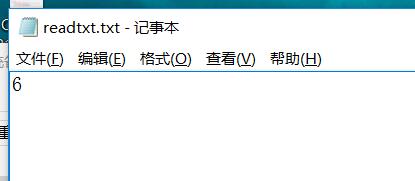
- 语法简洁,自动资源管理
readAllLines()适合小文件,lines()用流处理大文件
使用 Scanner(解析结构化文本)
import java.io.File;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class ReadTxtFile {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try (Scanner scanner = new Scanner(new File("example.txt"))) {
while (scanner.hasNextLine()) {
String line = scanner.nextLine();
System.out.println(line);
// 示例:按空格分割内容
String[] words = line.split(" ");
// 处理单词...
}
} catch (Exception e) {
System.err.println("错误: " + e.getMessage());
}
}
}
适用场景:
- 需按分隔符(空格/逗号等)解析内容
- 读取混合数据类型(如文本+数字)
关键注意事项
-
异常处理
- 必须捕获
IOException或FileNotFoundException - 文件路径错误是常见问题(建议使用绝对路径或检查相对路径)
- 必须捕获
-
资源释放
- 使用 try-with-resources(如
try (BufferedReader ...))自动关闭流,避免内存泄漏
- 使用 try-with-resources(如
-
字符编码
- 中文乱码?指定编码格式:
new InputStreamReader(new FileInputStream(path), "UTF-8")
- 中文乱码?指定编码格式:
-
文件路径写法
- 项目根目录:
src/example.txt - 绝对路径:
C:/data/example.txt(Windows)或/home/user/file.txt(Linux)
- 项目根目录:
最佳实践选择
| 场景 | 推荐方法 | 理由 |
|---|---|---|
| 大文件逐行处理 | BufferedReader |
缓冲提升性能 |
| 小文件快速读取 | Files.readAllLines() |
代码最简洁 |
| 需按格式解析内容 | Scanner |
支持正则和数据类型转换 |
| Java 8+ 流式处理 | Files.lines().forEach() |
函数式编程,易于链式操作 |
常见问题解决
- 文件不存在? → 用
File.exists()提前检查 - 权限不足? → 确保程序有文件读取权限 乱码?** → 统一使用UTF-8编码创建/读取文件
引用说明:
Oracle官方文档 Java I/O Tutorial
《Effective Java》第三版(Joshua Bloch)资源管理建议
编码规范参考Google Java Style Guide