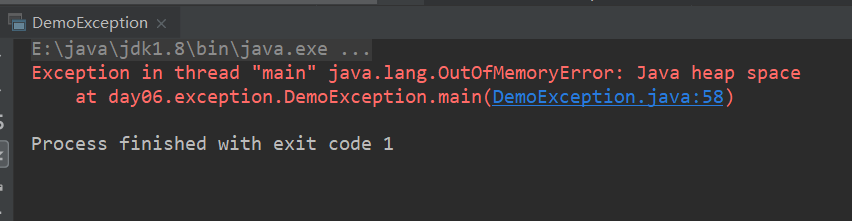
java错误 英文怎么说
- 后端开发
- 2025-08-22
- 19
核心术语解析
| 中文概念 | 英文对应词 | 使用场景示例 | 语法结构特点 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 语法错误 | Syntax Error |
编译阶段因不符合语言规范触发 | 缺少分号、括号不匹配等 |
| 运行时异常 | Runtime Exception |
JVM执行过程中发生的非受检型错误 | NullPointerException, ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException |
| 逻辑缺陷 | Logical Error |
代码能运行但结果不符合预期 | 算法设计失误、条件判断错误 |
| 编译时错误 | Compilation Error |
源代码无法通过编译器检查 | 类型不兼容、未定义变量 |
| 资源泄漏 | Resource Leak |
未正确释放文件句柄/数据库连接等资源 | 常见于try-with-resources缺失的场景 |
典型错误分类对照表
| 错误类型 | 英文全称 | 缩写/简称 | 示例场景 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 空指针引用 | NullPointerException |
NPE | 调用未初始化对象的方法或属性 |
| 数组越界 | ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException |
AIOOBE | 访问索引超过数组长度(如arr[10]当长度为5) |
| 类未找到 | ClassNotFoundException |
CNF | 动态加载不存在的类文件时发生 |
| 输入输出异常 | IOException |
文件读写失败、网络中断等I/O操作相关问题 | |
| 数值格式转换失败 | NumberFormatException |
NFE | 将非数字字符串解析为整数(如Integer.parseInt("abc")) |
技术场景中的实用表达
在实际开发中,工程师会根据上下文选择不同的表述方式:
-
通用描述
“There is a Java error in the code.”(代码中存在一个Java错误)
“The program threw a Java exception.”(程序抛出了一个Java异常) -
具体定位
“ANullPointerExceptionoccurred at line 42.”(第42行发生了空指针异常)
“Fix the compilation error related to missing semicolons.”(修复因缺少分号导致的编译错误)
-
调试建议
“Check for potential resource leaks using try-with-resources syntax.”(使用try-with-resources语法检查潜在的资源泄漏)
“Validate array bounds before accessing elements to avoid AIOOBE.”(在访问数组元素前验证下标范围以避免越界异常)
常见误区澄清
| 误解 | 真相 |
|---|---|
| “所有错误都是Exception子类” | 错误分为Error(严重系统级问题如栈溢出)和Exception(可捕获处理的异常)两大类 |
| “catch块必须指定具体异常类型” | 多catch分支应按从具体到通用的顺序排列(如先捕获SQLException再捕获Exception) |
| “finally块总会执行” | ️ 仅当JVM正常关闭时生效;若系统强制终止则不会执行 |
代码示例对比
易错写法(导致潜在错误)
public class BadExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] arr = new int[3];
System.out.println(arr[3]); // 触发ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException
}
}
正确实践(防御性编程)
public class GoodPractice {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
int[] arr = new int[3];
if (index >= 0 && index < arr.length) {
System.out.println(arr[index]);
} else {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Invalid array index: " + index);
}
} catch (IllegalArgumentException e) {
System.err.println("Caught custom validation error: " + e.getMessage());
} finally {
// Cleanup resources if any
}
}
}
FAQs
Q1: How to distinguish between checked and unchecked exceptions in Java?
A: Checked exceptions (e.g., IOException, SQLException) must be declared in method signatures using throws keyword or handled via try-catch. Unchecked exceptions (all subclasses of RuntimeException like NullPointerException) do not require explicit handling but represent programming logic flaws that should ideally be fixed rather than caught.
Q2: What’s the difference between Error and Exception classes?
A: The Error hierarchy (e.g., OutOfMemoryError, StackOverflowError) indicates serious system-level problems that applications should not attempt to recover from. In contrast, Exception and its subclasses represent conditions that may allow graceful recovery (e.g., retrying failed network requests after catching SocketTimeoutException).