上一篇
linux 如何 监听 端口
- Linux
- 2025-07-28
- 4
Linux 中,可以使用
netstat、
ss 或
lsof 命令监听端口。
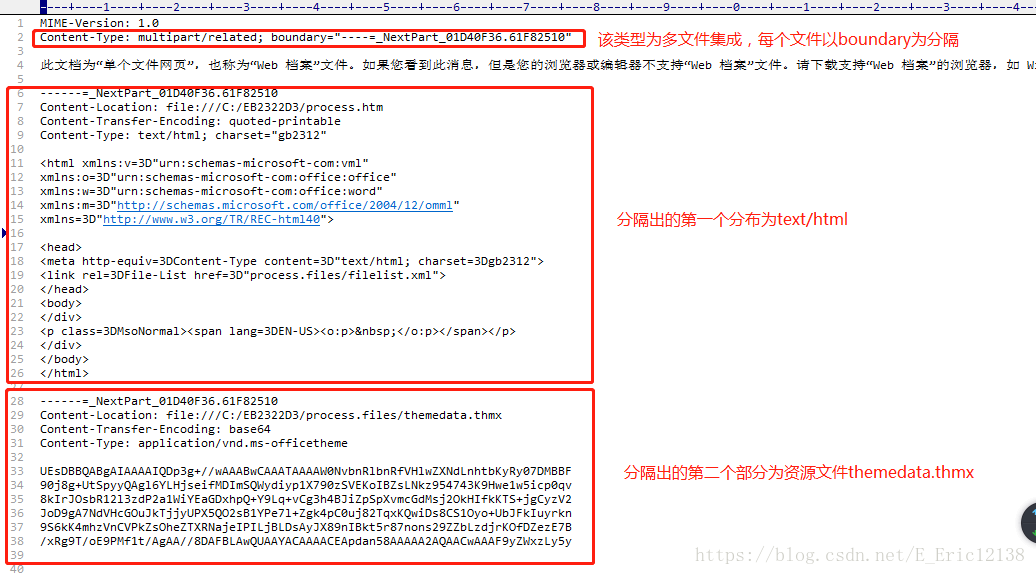
Linux 系统中,监听端口是一项常见的任务,通常用于服务器管理、网络服务配置和安全监控,以下是几种在 Linux 上监听端口的常用方法和工具:
使用 netstat 命令
netstat 是一个强大的网络统计工具,可以显示网络连接、路由表、接口统计等信息,要监听某个端口,可以使用以下命令:
netstat -tuln
-t:显示 TCP 端口-u:显示 UDP 端口-l:只显示监听状态的端口-n:以数字形式显示地址和端口号
示例输出:
| Proto | Local Address | Foreign Address | State |
|---|---|---|---|
| tcp | 0.0.0:80 | 0.0.0: | LISTEN |
| tcp | 0.0.1:631 | 0.0.0: | LISTEN |
| udp | 0.0.0:68 | 0.0.0: |
使用 ss 命令
ss 是 netstat 的现代替代品,提供了更详细和更快的信息,要监听端口,可以使用以下命令:
ss -tuln
示例输出:
State Recv-Q Send-Q Local Address:Port Peer Address:Port LISTEN 0 128 :80 : LISTEN 0 128 :22 : LISTEN 0 128 127.0.0.1:631 :
使用 lsof 命令
lsof(List Open Files)可以显示打开的文件和网络连接,要监听端口,可以使用以下命令:
lsof -i :80
示例输出:
COMMAND PID USER FD TYPE DEVICE SIZE/OFF NODE NAME nginx 1090 root 6u IPv4 5844 0t0 TCP :80 (LISTEN)
使用 nmap 命令
nmap 是一个网络扫描工具,可以用来扫描端口,要扫描某个端口,可以使用以下命令:
nmap -p 80 localhost
示例输出:
Starting Nmap 7.80 ( https://nmap.org ) at 2023-10-01 12:00 PDT Nmap scan report for localhost (127.0.0.1) Host is up (0.000010s latency). PORT STATE SERVICE 80/tcp open http Nmap done: 1 IP address (1 host up) scanned in 0.02 seconds
使用 iptables 命令
iptables 是 Linux 上的防火墙工具,可以用来监听和过滤网络流量,要查看规则,可以使用以下命令:
iptables -L -v -n
示例输出:
Chain INPUT (policy ACCEPT 0 packets, 0 bytes)
pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination
0 0 ACCEPT all - any any anywhere anywhere state NEW,ESTABLISHED
0 0 ACCEPT tcp - any any anywhere 192.168.1.0/24 tcp dpt:80
使用 systemctl 命令
如果你使用的是 systemd,可以通过 systemctl 来管理服务并监听端口,要检查 Nginx 服务的状态,可以使用以下命令:
systemctl status nginx
示例输出:
● nginx.service A high performance web server and a reverse proxy server Loaded: loaded (/lib/systemd/system/nginx.service; enabled; vendor preset: enabled) Drop-In: /run/systemd/generator.conf-30-nginx.conf Drop-In: /run/systemd/generator.conf-31-nginx.conf Drop-In: /run/systemd/generator.conf-32-nginx.conf Drop-In: /run/systemd/generator.conf-33-nginx.conf Drop-In: /run/systemd/generator.conf-34-nginx.conf Drop-In: /run/systemd/generator.conf-35-nginx.conf Drop-In: /run/systemd/generator.conf-36-nginx.conf Drop-In: /run/systemd/generator.conf-37-nginx.conf Drop-In: /run/systemd/generator.conf-38-nginx.conf Drop-In: /run/systemd/generator.conf-39-nginx.conf Drop-In: /run/systemd/generator.conf-40-nginx.conf Drop-In: /run/systemd/generator.conf-41-nginx.conf Drop-In: /run/systemd/generator.conf-42-nginx.conf Drop-In: /run/systemd/generator.conf-43-nginx.conf Drop-In: /run/systemd/generator.conf-44-nginx.conf Drop-In: /run/systemd/generator.conf-45-nginx.conf Drop-In: /run/systemd/generator.conf-46-nginx.conf Drop-In: /run/systemd/generator.conf-47-nginx.conf Drop-In: /run/systemd/generator.conf-48-nginx.conf Drop-In: /run/systemd/generator.conf-49-nginx.conf Drop-In: /run/systemd/generator.conf-50-nginx.conf Drop-In: /run/systemd/generator.conf-51-nginx.conf Drop-In: /run/systemd/generator.conf-52-nginx.conf Drop-In: /run/systemd/generator.conf-53-nginx.conf Drop-In: /run/systemd/generator.conf-54-nginx.conf Drop-In: /run/systemd/generator.