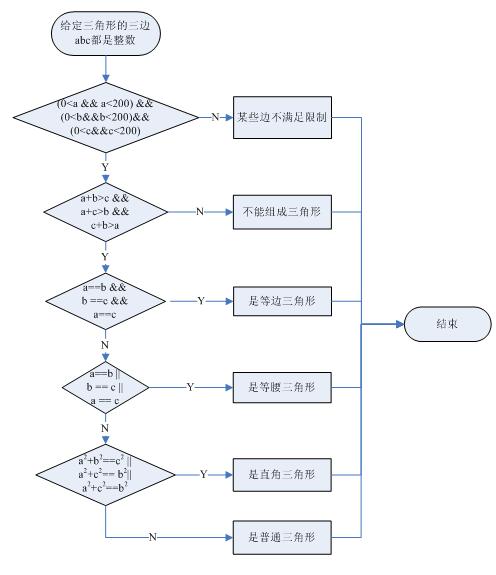
主从表在java中怎么定义
- 后端开发
- 2025-07-29
- 5
Java中,主从表(也称为一对多关系)的定义和处理通常涉及数据库设计、实体类映射以及数据访问层的实现,以下是详细的步骤和示例,帮助你理解如何在Java中定义和操作主从表。
数据库设计
需要在数据库中设计主表和从表,确保它们之间通过外键建立关联。
示例:
假设我们有一个部门(Department)和员工(Employee)的主从关系,一个部门可以有多个员工,但一个员工只能属于一个部门。
SQL脚本:
CREATE TABLE Department (
id BIGINT PRIMARY KEY AUTO_INCREMENT,
name VARCHAR(100) NOT NULL
);
CREATE TABLE Employee (
id BIGINT PRIMARY KEY AUTO_INCREMENT,
name VARCHAR(100) NOT NULL,
department_id BIGINT,
FOREIGN KEY (department_id) REFERENCES Department(id)
);
实体类定义
使用Java Persistence API(如JPA或Hibernate)来定义实体类,并设置它们之间的关系。
Department实体类:
import javax.persistence.;
import java.util.Set;
@Entity
@Table(name = "Department")
public class Department {
@Id
@GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.IDENTITY)
private Long id;
@Column(nullable = false)
private String name;
// 主从关系:一个部门有多个员工
@OneToMany(mappedBy = "department", cascade = CascadeType.ALL, orphanRemoval = true)
private Set<Employee> employees;
// 构造方法、Getter和Setter
public Department() {}
public Department(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
// Getters and Setters
public Long getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(Long id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public Set<Employee> getEmployees() {
return employees;
}
public void setEmployees(Set<Employee> employees) {
this.employees = employees;
}
}
Employee实体类:
import javax.persistence.;
@Entity
@Table(name = "Employee")
public class Employee {
@Id
@GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.IDENTITY)
private Long id;
@Column(nullable = false)
private String name;
// 外键关联到Department
@ManyToOne(fetch = FetchType.LAZY)
@JoinColumn(name = "department_id")
private Department department;
// 构造方法、Getter和Setter
public Employee() {}
public Employee(String name, Department department) {
this.name = name;
this.department = department;
}
// Getters and Setters
public Long getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(Long id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public Department getDepartment() {
return department;
}
public void setDepartment(Department department) {
this.department = department;
}
}
数据访问层(Repository)
使用Spring Data JPA,可以轻松创建数据访问接口。
DepartmentRepository接口:
import org.springframework.data.jpa.repository.JpaRepository;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Repository;
import java.util.Optional;
@Repository
public interface DepartmentRepository extends JpaRepository<Department, Long> {
Optional<Department> findByName(String name);
}
EmployeeRepository接口:
import org.springframework.data.jpa.repository.JpaRepository;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Repository;
import java.util.List;
@Repository
public interface EmployeeRepository extends JpaRepository<Employee, Long> {
List<Employee> findByDepartmentId(Long departmentId);
}
服务层(Service)
在服务层中,处理业务逻辑,包括保存、更新和删除主从表的数据。
DepartmentService示例:
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import org.springframework.transaction.annotation.Transactional;
import java.util.Optional;
import java.util.Set;
@Service
public class DepartmentService {
@Autowired
private DepartmentRepository departmentRepository;
@Autowired
private EmployeeRepository employeeRepository;
// 添加部门及其员工
@Transactional
public Department addDepartmentWithEmployees(Department department, Set<Employee> employees) {
department.setEmployees(employees);
for (Employee emp : employees) {
emp.setDepartment(department);
}
return departmentRepository.save(department);
}
// 根据ID获取部门及其员工
public Optional<Department> getDepartmentWithEmployees(Long id) {
return departmentRepository.findById(id);
}
// 删除部门及其所有员工
@Transactional
public void deleteDepartment(Long id) {
departmentRepository.deleteById(id);
}
}
控制器层(Controller)
提供API接口,供前端调用。
DepartmentController示例:
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.http.ResponseEntity;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.;
import java.util.Optional;
import java.util.Set;
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/api/departments")
public class DepartmentController {
@Autowired
private DepartmentService departmentService;
// 创建部门及员工
@PostMapping("/")
public ResponseEntity<Department> createDepartment(@RequestBody Department department, @RequestParam Set<Employee> employees) {
Department savedDepartment = departmentService.addDepartmentWithEmployees(department, employees);
return ResponseEntity.ok(savedDepartment);
}
// 获取部门及员工详情
@GetMapping("/{id}")
public ResponseEntity<Department> getDepartment(@PathVariable Long id) {
Optional<Department> optionalDept = departmentService.getDepartmentWithEmployees(id);
return optionalDept.map(ResponseEntity::ok).orElseGet(() -> ResponseEntity.notFound().build());
}
// 删除部门及员工
@DeleteMapping("/{id}")
public ResponseEntity<Void> deleteDepartment(@PathVariable Long id) {
departmentService.deleteDepartment(id);
return ResponseEntity.noContent().build();
}
}
注意事项与最佳实践
-
懒加载(Lazy Loading): 默认情况下,
@OneToMany关系使用懒加载,避免不必要的数据加载,根据需求,可以调整fetch属性,将FetchType.LAZY改为FetchType.EAGER以立即加载相关数据。 -
级联操作(Cascade): 在
@OneToMany注解中使用cascade = CascadeType.ALL,确保对主表的操作(如保存、删除)自动应用到从表。orphanRemoval = true允许在移除主表记录时,自动删除无主的从表记录。 -
双向关联 vs 单向关联: 上述示例展示了双向关联(
Department知道Employee,Employee也知道Department),在某些场景下,单向关联可能更合适,具体取决于业务需求。 -
DTO与实体分离: 为了安全性和灵活性,建议在控制器层使用数据传输对象(DTO),而不是直接暴露实体类,这有助于防止客户端直接修改实体,并允许自定义返回的数据结构。
-
事务管理: 对于涉及多个数据库操作的业务逻辑,使用事务管理(如
@Transactional)确保数据的一致性和完整性。 -
异常处理: 实现全局异常处理机制,捕获并处理可能出现的数据库异常,如唯一约束冲突、外键约束失败等。
示例流程
创建部门及员工:
- 发送POST请求到
/api/departments/,请求体包含部门信息和员工列表。 DepartmentService处理请求,设置部门与员工的关联关系,并保存到数据库。- 返回保存后的部门信息,包括关联的员工。
获取部门及员工详情:
- 发送GET请求到
/api/departments/{id}。 DepartmentService根据ID查询部门,并加载关联的员工。- 返回部门及其员工的详细信息。
删除部门及员工:
- 发送DELETE请求到
/api/departments/{id}。 DepartmentService删除指定部门,由于设置了orphanRemoval = true,关联的员工也会被删除。- 返回204 No Content状态码。
FAQs常见问题解答
问题1:如何处理主从表中的批量插入?
- 解答: 可以使用批量操作来提高性能,使用
JdbcTemplate的batchUpdate方法,或者在Service层中遍历集合并逐个保存,确保事务管理正确,以避免部分插入成功导致数据不一致。
问题2:在主从关系中,如何避免循环引用?
- 解答: 如果采用双向关联,可能会在序列化(如JSON转换)时出现循环引用的问题,为避免这种情况,可以在实体类中使用
@JsonManagedReference和@JsonBackReference注解,或者使用DTO来控制数据的