上一篇
安卓形状图像识别
- 行业动态
- 2025-04-22
- 4
技术选型与核心流程
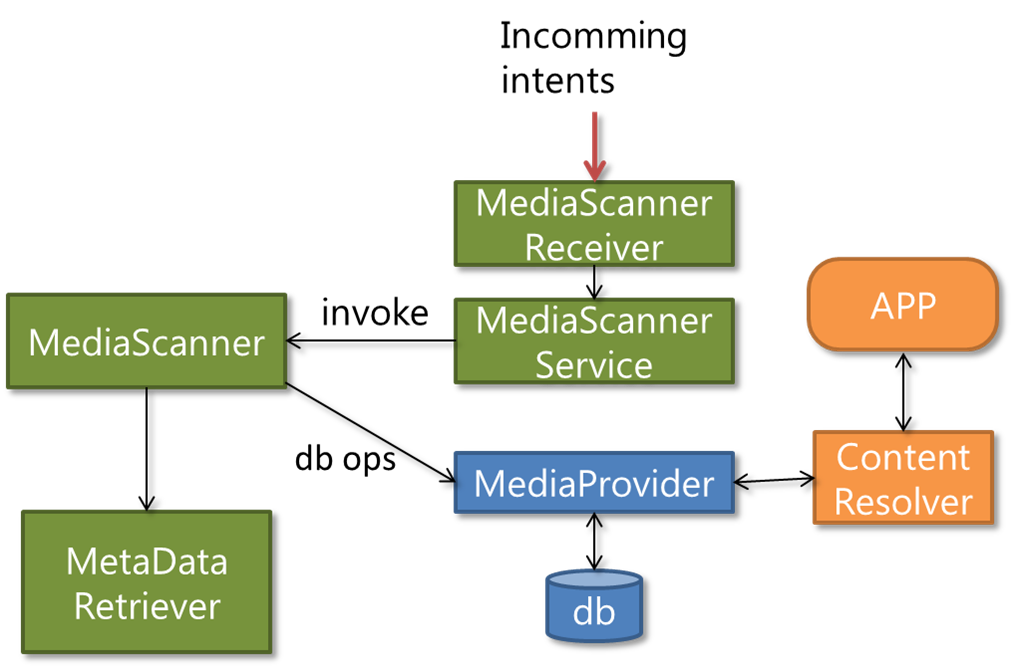
在安卓中实现形状图像识别,通常结合 OpenCV(图像处理)和 TensorFlow Lite/ML Kit(模型推理)完成,以下是关键技术点:
| 模块 | 功能描述 |
|---|---|
| 图像采集 | 通过摄像头或本地文件获取图像,需处理权限(CAMERA/READ_EXTERNAL_STORAGE)。 |
| 预处理 | 灰度化、二值化、降噪、边缘检测(如Canny算法)。 |
| 形状检测 | 轮廓提取(findContours)、多边形逼近(approxPolyDP)。 |
| 特征分类 | 基于几何特征(面积、周长、顶点数)或机器学习模型(如CNN)判断形状类别。 |
图像预处理步骤
- 灰度化:将彩色图像转为灰度图,降低计算复杂度。
Mat gray = new Mat(); Imgproc.cvtColor(inputImage, gray, Imgproc.COLOR_BGR2GRAY);
- 二值化:通过阈值分割突出目标形状。
Mat binary = new Mat(); Imgproc.threshold(gray, binary, 127, 255, Imgproc.THRESH_BINARY);
- 降噪与边缘检测:
Mat edges = new Mat(); Imgproc.GaussianBlur(binary, binary, new Size(5, 5), 0); // 高斯模糊 Imgproc.Canny(binary, edges, 50, 150); // Canny边缘检测
形状检测与分类逻辑
- 轮廓提取:
List<MatOfPoint> contours = new ArrayList<>(); Mat hierarchy = new Mat(); Imgproc.findContours(edges, contours, hierarchy, Imgproc.RETR_EXTERNAL, Imgproc.CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE);
- 轮廓筛选与多边形逼近:
过滤小面积噪声,保留最大轮廓,并通过approxPolyDP逼近形状:double maxArea = 0; int maxIndex = -1; for (int i = 0; i < contours.size(); i++) { double area = Imgproc.contourArea(contours.get(i)); if (area > maxArea) { maxArea = area; maxIndex = i; } } MatOfPoint2f approxCurve = new MatOfPoint2f(); Imgproc.approxPolyDP(new MatOfPoint2f(contours.get(maxIndex).toArray()), approxCurve, 0.02 Imgproc.arcLength(contours.get(maxIndex), true), true); - 形状判断:
- 三角形:顶点数 ≈ 3,且面积/周长比符合阈值。
- 矩形/正方形:顶点数 ≈ 4,且宽高比接近1(正方形)或任意比例(矩形)。
- 圆形:顶点数 ≥ 5且轮廓圆润(通过圆度计算)。
int vertices = (int) approxCurve.total(); if (vertices == 3) { return "Triangle"; } else if (vertices == 4) { // 计算宽高比判断是否为正方形 Rect boundingRect = Imgproc.boundingRect(contours.get(maxIndex)); double aspectRatio = (double) boundingRect.width / boundingRect.height; if (aspectRatio >= 0.9 && aspectRatio <= 1.1) { return "Square"; } else { return "Rectangle"; } } else if (vertices >= 5) { // 计算圆度(周长^2 / (4π面积)) double perimeter = Imgproc.arcLength(new MatOfPoint2f(contours.get(maxIndex).toArray()), true); double circularity = (perimeter perimeter) / (4 Math.PI maxArea); if (circularity < 1.2) { // 阈值可调 return "Circle"; } } return "Unknown";
性能优化策略
| 优化方向 | 具体措施 |
|---|---|
| 降分辨率处理 | 将图像缩放至合理尺寸(如800×600),减少计算量。 |
| 多线程处理 | 使用 AsyncTask 或 ExecutorService 将图像处理放在子线程。 |
| 硬件加速 | 启用 OpenCV 的 NEON/ARM 优化,或使用 GPU 加速库(如 OpenCL)。 |
| 模型轻量化 | 若用深度学习模型,选择 MobileNet、EfficientNet 等轻量级结构,或使用 TFLite。 |
代码示例(核心逻辑)
// 1. 初始化OpenCV
System.loadLibrary("opencv_java4");
// 2. 预处理与轮廓提取
Mat gray = new Mat();
Imgproc.cvtColor(inputImage, gray, Imgproc.COLOR_BGR2GRAY);
Imgproc.GaussianBlur(gray, gray, new Size(5, 5), 0);
Imgproc.Canny(gray, edges, 50, 150);
List<MatOfPoint> contours = new ArrayList<>();
Imgproc.findContours(edges, contours, new Mat(), Imgproc.RETR_EXTERNAL, Imgproc.CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE);
// 3. 筛选最大轮廓并分类
if (!contours.isEmpty()) {
MatOfPoint2f approxCurve = new MatOfPoint2f();
Imgproc.approxPolyDP(new MatOfPoint2f(contours.get(0).toArray()), approxCurve, 0.02 Imgproc.arcLength(contours.get(0), true), true);
int vertices = (int) approxCurve.total();
// 根据顶点数和几何特征分类(见上方逻辑)
}
问题与解答
问题1:如何提高圆形识别的准确率?
解答:
- 优化圆度计算:调整圆度阈值(如
circularity < 1.1),或结合轮廓圆润度(如检查轮廓点到中心的均方差)。 - 形态学处理:使用
HoughCircles检测圆形,补充规则方法的不足。 - 数据增强:若用机器学习模型,增加不同光照、旋转的圆形样本,提升模型鲁棒性。
问题2:如何处理旋转后的形状识别?
解答:
- 旋转不变特征:使用 Hu矩(
HuMoments)作为特征,其对旋转、缩放不敏感。 - 轮廓对齐:将轮廓的主方向对齐到坐标轴(如通过
minRect计算旋转角度并校正)。 - 深度学习模型:训练旋转不变的CNN模型(如添加数据增强中的随机旋转