从数据库中获取如JSON
- 行业动态
- 2025-04-04
- 6
“
json,{, "data": [, {, "id": 1,, "name": "John Doe",, "email": "john.doe@example.com", },, {, "id": 2,, "name": "Jane Smith",, "email": "jane.smith@example.com", }, ],},“
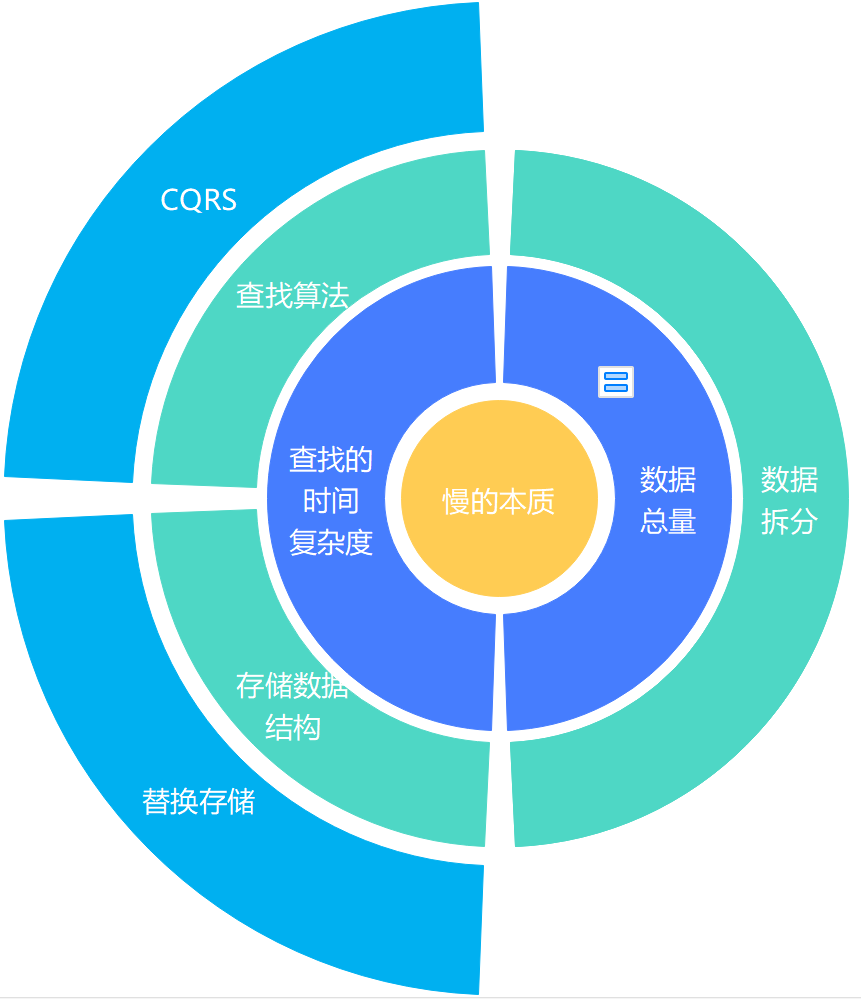
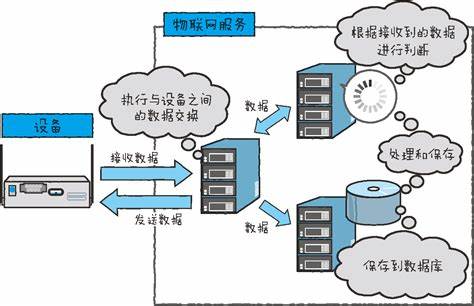
在现代Web开发中,从数据库获取数据并将其转换为JSON格式是一项常见任务,这通常涉及以下几个步骤:连接到数据库、执行查询、处理结果集以及将结果转换为JSON格式,以下是一个详细的指南,介绍如何从不同类型的数据库(如MySQL、PostgreSQL和MongoDB)中获取数据并以JSON格式返回。
使用MySQL数据库
安装必要的库
确保你已经安装了MySQL的Python库mysql-connector-python。
pip install mysql-connector-python
连接到数据库并获取数据
以下是一个简单的示例,展示如何连接到MySQL数据库并获取数据:
import mysql.connector
import json
连接到数据库
conn = mysql.connector.connect(
host="localhost",
user="yourusername",
password="yourpassword",
database="yourdatabase"
)
cursor = conn.cursor(dictionary=True)
执行查询
query = "SELECT FROM yourtable"
cursor.execute(query)
获取结果
results = cursor.fetchall()
转换为JSON
json_data = json.dumps(results, default=str)
关闭连接
cursor.close()
conn.close()
print(json_data)
使用PostgreSQL数据库
安装必要的库
确保你已经安装了PostgreSQL的Python库psycopg2。
pip install psycopg2-binary
连接到数据库并获取数据
以下是一个示例,展示如何连接到PostgreSQL数据库并获取数据:
import psycopg2
import json
连接到数据库
conn = psycopg2.connect(
host="localhost",
database="yourdatabase",
user="yourusername",
password="yourpassword"
)
cursor = conn.cursor(cursor_factory=psycopg2.extras.DictCursor)
执行查询
query = "SELECT FROM yourtable"
cursor.execute(query)
获取结果
results = cursor.fetchall()
转换为JSON
json_data = json.dumps(results, default=str)
关闭连接
cursor.close()
conn.close()
print(json_data)
使用MongoDB数据库
安装必要的库
确保你已经安装了MongoDB的Python库pymongo。
pip install pymongo
连接到数据库并获取数据
以下是一个示例,展示如何连接到MongoDB数据库并获取数据:
from pymongo import MongoClient
import json
连接到数据库
client = MongoClient("mongodb://localhost:27017/")
db = client["yourdatabase"]
collection = db["yourcollection"]
获取数据
results = collection.find()
转换为JSON
json_data = json.dumps(list(results), default=str)
print(json_data)
使用SQLite数据库
安装必要的库
确保你已经安装了SQLite的Python库sqlite3(这是Python标准库的一部分)。
无需额外安装
连接到数据库并获取数据
以下是一个示例,展示如何连接到SQLite数据库并获取数据:
import sqlite3
import json
连接到数据库
conn = sqlite3.connect('yourdatabase.db')
cursor = conn.cursor()
执行查询
query = "SELECT FROM yourtable"
cursor.execute(query)
获取结果
results = cursor.fetchall()
columns = [description[0] for description in cursor.description]
json_data = [dict(zip(columns, row)) for row in results]
转换为JSON
json_data = json.dumps(json_data, default=str)
关闭连接
cursor.close()
conn.close()
print(json_data)
FAQs(常见问题解答)
Q1: 如何处理数据库连接错误?
A1: 在实际应用中,应添加异常处理代码来捕获和处理数据库连接错误,可以使用try...except块来捕获异常并记录错误信息或采取其他补救措施。
try:
conn = mysql.connector.connect(host="localhost", user="yourusername", password="yourpassword", database="yourdatabase")
except mysql.connector.Error as err:
print(f"Error: {err}")
Q2: 如果数据库表包含大量数据,如何优化性能?
A2: 如果数据库表包含大量数据,可以考虑以下几点来优化性能:
分页查询:只获取部分数据而不是一次性加载所有数据,在MySQL中使用LIMIT和OFFSET关键字。
索引:确保对经常查询的列建立索引,以提高查询速度。
异步处理:对于需要长时间运行的查询,考虑使用异步处理方式。